As artificial intelligence (AI) changes, hackers and cybersecurity teams are both taking advantage of it. AI can actively observe, examine, identify, and react to cyber dangers instantaneously. AI algorithms utilize extensive data analysis to identify trends that signal a potential cyber threat. Additionally, they may thoroughly examine the entire network to identify vulnerabilities and proactively thwart typical cyberattacks.
Most people have encountered artificial intelligence (AI) in the past few days, whether it was via a car’s GPS, an email’s auto-correct feature, or an online search. So, let’s go over the fundamentals of AI, how hackers and cybersecurity teams are utilizing it, and what you can do to be safe.
What Is AI?
AI encompasses a wide range of fields that study how to make computers smarter so that they can do tasks normally performed by humans. Because of this, AI machines would be able to do jobs that were previously reserved for humans. There are some jobs that AI could do better than humans.
Finding the optimal solution to a problem or means to accomplish a goal is something that many artificial intelligence (AI) devices want to do. For the most part, they achieve this by sifting through mountains of training data in search of trends that they can incorporate into their decision-making process.
Artificial intelligence (AI) may sound far-fetched, yet its origins can be traced back to 1950, when Alan Turing, a British mathematician and logician, pondered the possibility of “thinking machines” with human-like reasoning abilities.1 The phrase “artificial intelligence” was coined a few years later.
AI In Cybersecurity
AI, or Artificial Intelligence, has fundamentally transformed the mindset of IT security experts when it comes to cybersecurity. Advanced AI-driven cybersecurity tools and systems can enhance data protection against threats by swiftly identifying behavior patterns, automating procedures, and detecting anomalies.
AIbasically observes and analyzes patterns of behavior. By utilizing these patterns as a foundation, AIcan identify atypical activities and prevent unwanted entry into systems. AI can assist in prioritizing risk and promptly identify the potential for viruses and intrusions prior to their occurrence.
When AI is effectively deployed, it can act as the driving force behind security automation, thereby relieving staff of monotonous chores and allowing them to allocate their time and resources more efficiently. AI has the ability to decrease the frequency of human mistakes by eliminating the involvement of humans in a task or process.
Why Is AI In Cybersecurity Important?
The significance of AI in cybersecurity lies in its ability to enhance and strengthen the protection of digital systems and networks against malicious activities and threats.
Enterprises involved in cybercrime have already allocated resources towards the use of machine learning, automation, and AIin order to carry out extensive and focused cyberattacks against other enterprises. The frequency of threats and the likelihood of ransomware affecting networks is steadily increasing.
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are enabling security analysts to achieve a balanced and fair competition by efficiently handling vast quantities of data, delivering quick and valuable insights through analysis, and effectively filtering out the excessive number of daily security warnings and false positives. This significantly enhanced the efficiency and production of your staff, providing them with a competitive edge against potential cyber criminals.
Due to the emergence of advanced attack methods like polymorphic malware, scripting, and “living-off-the-land” attacks, criminals may now more easily evade classic anti-virus defenses that rely on file scanning. In order to safeguard against the development of malware, cybersecurity is increasingly adopting advanced techniques such as behavior analysis. Behavior analysis and detection methods are highly effective, as every malware ultimately requires displaying bad behavior in order to achieve its objectives. Artificial intelligence, when adequately trained, possesses the potential to efficiently observe, identify, and react to these malevolent actions at a quicker pace than humans alone.
Why And How AI Can Improve Cybersecurity?
Modern AI systems are specifically taught to identify and detect possible cyber threats, as well as discover new methods that attackers may use to compromise the sensitive data of your business. These systems are designed to protect and secure your company’s valuable information. The utilization of AI-driven cybersecurity tools offers three primary advantages:
- Examining a lot of data quickly
- Identifying irregularities and weaknesses
- Implementing automated procedures for repetitive duties
The cybersecurity business is not immune to the widespread impact of artificial intelligence (AI). According to a recent study, the worldwide market for cybersecurity products powered by AIwas valued at $15 billion in 2021 and is projected to reach to $135 billion by 2030.
In addition to conventional tools utilized for identity and access management, risk management, intrusion detection, and data loss prevention, cybersecurity organizations are progressively placing more trust in artificial intelligence (AI). The ability of AI to sift through massive amounts of data in search of patterns makes it well-suited to jobs like:
- Identifying real attacks with higher accuracy than humans, with fewer false-positives, and answers prioritized according to their actual risks;
- Recognizing and marking as malicious the specific email and message formats used in phishing attacks;
- Security teams can better detect vulnerabilities prior to cybercriminals exploiting them by simulating social engineering attacks and
- They were quickly analyzing massive volumes of incident-related data to enable security teams to respond to threats with confidence.
Also, artificial intelligence (AI) might revolutionize penetration testing, which involves purposefully attacking software and network defenses to find vulnerabilities. Organizations can better protect themselves from cyberattacks by creating artificial intelligence tools that specifically target their own technology.
Cybersecurity organizations would greatly benefit from this intelligence if they could use it to prevent future attacks. Businesses could save money on information technology (IT) expenditures and better safeguard customer and company data if breaches could be prevented before they happened.
The possibilities of using AI in cybersecurity are nearly limitless. The speed and precision of identifying and addressing threats are enhanced to achieve near real-time results. Artificial intelligence (AI) can assist in reducing the consequences of a ransomware attack by promptly alerting your security team to any questionable activity. Lastly, artificial intelligence enhances the efficiency of cybersecurity operations by automating processes, thereby allowing your security staff to allocate their time and assets to more critical responsibilities.
What Distinguishes AI Cybersecurity From Other Type Of Cybersecurity?
The utilization of artificial intelligence in cybersecurity will never completely supplant security pros, as there will perpetually exist a necessity for innovative troubleshooting and tackling increasingly intricate obstacles in the professional environment. Nevertheless, artificial intelligence has the capability and is currently being utilized to support human security experts through the examination of extensive data sets, identification of patterns, and generation of valuable insights derived from substantial quantities of security information. The completion of this task using conventional security procedures may require several hours or even weeks.
Before the advent of artificial intelligence (AI), security professionals relied on signature-based detection techniques and algorithms to discern potential cyber threats. These security tools analyze incoming network traffic by cross-referencing it with a database of established threats or signatures of malicious code. When the system detects something, it immediately sends an alert and advises the security expert to take action to prevent or isolate the threat.
The utilization of signature-based security has proven to be rather efficient in mitigating known threats. Nevertheless, the utilization of the signature-based detection method has been found to need to be improved in countering emerging (Zero-Day) or unfamiliar risks. Frequently, these tools also led to an increased occurrence of false positives, causing security professionals to pursue fruitless investigations.
Conventional cybersecurity also mainly depends on manual analysis. Security analysts are required to conduct manual investigations of security alerts and event logs in order to identify any discernible trends that may indicate a potential security breach. Examining logs and events can be a time-consuming task, and it is a costly error for firms to rely entirely on one security analyst.
Artificial intelligence possesses the capability to rectify these deficiencies in conventional cybersecurity and accomplish even more. As this technology further develops, it will significantly influence cybersecurity procedures and individuals.
How Hackers Use AI
Cybercriminals are persistent and creative, which is a bad thing. Several of their uses of AI for their personal gain are as follows:
-
Using Social Engineering Techniques:
To get people to give up sensitive information or do other security-related mistakes, these schemes use psychological manipulation. Phishing, vishing, and corporate email compromise scams are all part of this wide category of fraudulent activities.
Cybercriminals can automate a lot of the social engineering processes with AI, and they can also make more sophisticated, targeted, and effective messages to trick people. Because of this, cybercriminals can launch more attacks with more success rate in less time.
-
Theft Of Passwords:
Hackers are using AI to make better password decryption algorithms. Hackers are able to increase their efficiency and profits thanks to the improved algorithms that provide faster and more precise password guessing. Hackers may start focusing even more on password hacking as a result of this.
-
Encounters With Deepfakes:
This form of deception takes advantage of AI’s natural talent for audio and visual content manipulation to create the illusion of authenticity. This involves impersonating someone else through the use of fake audio and video. The altered material can be quickly and easily shared online, even on powerful social media sites, in order to cause anxiety, panic, or confusion in the minds of those who see it.
Along with social engineering, extortion, and other forms of cybercrime, deepfakes are a powerful tool for cybercriminals.
-
Data Poisoning:
The training data utilized by an AI algorithm can be “poisoned” by hackers, who alter it in order to influence its final decisions. If the algorithm is receiving misleading data, it will produce inaccurate results. Data poisoning is also not always easy to spot, and it might take some time. The damage might be quite severe by the time it’s discovered.
How AI Enhances Managed Detection And Response (MDR)?
It is now essential to have security operations running constantly. However, the complex structures of contemporary workplaces and the speed with which cyber threats penetrate these settings make it nearly impossible for the majority of enterprises to effectively handle the detection and response process alone. Managed Detection and Response (MDR) is the solution for this situation.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are currently revolutionizing the manner in which security operations centers (SOCs) provide managed detection and response (MDR) as well as other managed security services. SOCS are enhancing their MDR capabilities, improving efficiency, and increasing resilience against constantly changing cyber threats by utilizing these technologies. By taking on more of the labor-intensive tasks associated with 24/7 threat detection and analysis, AI can help increase the speed and accuracy of MDR.
AI Is Now Making A Positive Impact On MDR In Four Main Areas:
-
Threat Detection And Intelligence
Deep neural networks are capable of training machines to detect and classify threats, such as malware. Artificial intelligence has the capability to gather, analyze, and enhance data related to potential dangers from many origins within a company. Furthermore, it has the capability to establish connections and analyze the data in order to generate threat profiles, check against indicators, and identify potential new risks. AI facilitates proactive threat detection, wherein security experts utilize sophisticated analytics and automation to detect concealed or unfamiliar risks inside a given setting.
-
Security Operations Center (SOC) Operations
Managed Detection and Response (MDR) providers recognize the significant potential of utilizing artificial intelligence (AI) to enhance and optimize the general functioning and operational efficiency of their Security Operations Centers (SOC). Managed security service providers have the capability to monitor and assess its SOC’s key performance indicators (KPIs), such as the amount of security alerts, response times, rates of resolution, and levels of client satisfaction. Artificial intelligence (AI) can assist in detecting and resolving security vulnerabilities, operational obstacles, or inefficiencies in the procedures, workflows, and tools of a managed Security Operations Center (SOC).
-
Cybersecurity Development And Training
Artificial intelligence can aid in evaluating and enhancing the relevant knowledge, abilities, and skills of SOC analysts. AI’s capacity for learning and ongoing improvement enables MDR vendors to develop exceptionally customized learning paths for staff. Furthermore, companies have the ability to develop and present captivating and lifelike security training exercises, simulations, and scenarios.
-
Advancements In Security:
The fundamental objective of AI, which is to constantly enhance its performance, makes it very suitable for assisting in the process of invention. The modern Security Operations Center (SOC) must possess the ability to rapidly adjust and enhance its capabilities in order to address evolving client requirements and the ever-changing landscape of threats. MDR providers may maintain a competitive advantage by leveraging AI and ML technologies, which help them stay ahead of the industry trends and mitigate potential risks.
Keep Your Data Safe In An Ever-Evolving AI Landscape
Concerns regarding data privacy, along with risk management, are on the rise as AI develops further. Policymakers are thinking about how to advance AI in a way that will have the most positive effects on society with the fewest possible drawbacks. However, at this time, no comprehensive federal legislation regarding artificial intelligence exists in the US.
To sum up, how does this impact you? From a safety standpoint, how do you see AI developments influencing your daily life?
Thankfully, it’s actually quite easy to figure out. No new cybersecurity regulations are required of you. Instead, you should assess the state of your cybersecurity measures and ensure that they adhere to industry standards in key areas like data privacy, passwords, personal cybersecurity, and, most importantly, social engineering.
The best way to stay up-to-date on AI news and cybersecurity tips is to check back with your Security Center on a frequent basis. If it can keep itself safe, then the rest of us will have an easier time taking advantage of the AI-powered improvements to our daily lives.
Basic Terms And Questions:
What is Machine Learning?
Machine Learning (ML) refers to the field of study that focuses on developing algorithms and models that enable computers to learn and make predictions or decisions without being manually programmed.
Machine learning largely concerns the ability of a machine to replicate intelligent human behavior. Data serves as the fundamental driving force behind machine learning. Computer learning employs mathematical models to facilitate autonomous learning by a computer without the need for explicit guidance or programming by a human. This implies that a system equipped with machine learning capabilities is capable of autonomously enhancing its performance by continuous learning from its own experiences, without the need for human involvement.
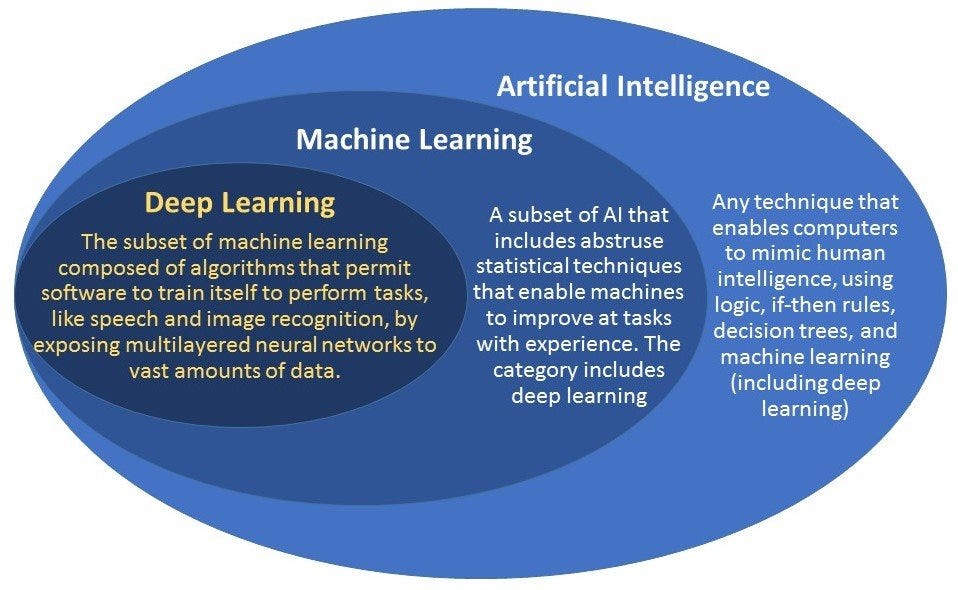
Artificial intelligence also includes machine learning, but the terms are not synonymous. Machine learning (ML) refers to artificial intelligence (AI) systems that have the capacity to acquire knowledge and adjust their behavior without significant human involvement or explicit programming.
What Are Deep Neural Networks?
Deep neural networks are complex computational models that are designed to mimic the structure and functioning of the human brain. They consist of multiple layers of interconnected artificial neurons, which allow them to process and analyze large amounts of data in a structured way.
Deep learning is an advanced form of machine learning that utilizes neural networks to mimic the cognitive process in the human brain. A neural network utilizes machine learning and artificial intelligence to instruct machines on how to analyze data in a manner that is influenced by the human brain. A neural network, similar to the human brain, is composed of functional layers. Within these layers, specific actions, tasks, or processes evoke an accurate reaction from the machine. The greater the number of layers in the neural network, the more eloquent and advanced the answer becomes.
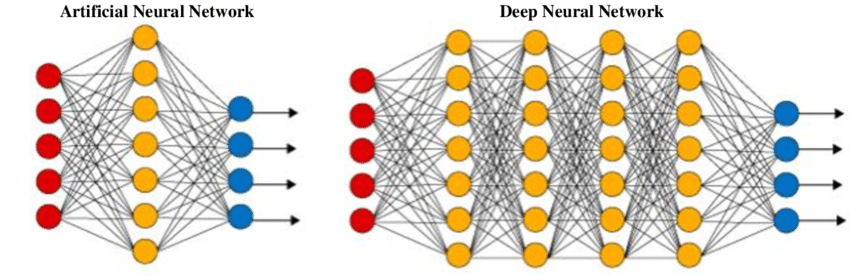
Deep neural networks refer to neural networks that have numerous hidden layers. Neural network algorithms are programmed to stick to a predetermined set of rules by making predictions and drawing conclusions based on past iterations and experiences. An adaptable system that allows machines to learn from their errors and keep getting better is created by a deep neural network. Deep neural networks possess the capacity to address complex problems that conventional machine learning methods cannot, such as effectively summarizing materials or accurately identifying faces.
What Are The Potential Hazards Associated With The Use Of AI In Cybersecurity?
It is crucial to keep in mind that artificial intelligence (AI) is still in its early stages as a technology. Artificial intelligence still relies on human intervention, not just for the purpose of training AI engines but also to intervene when an engine makes an error. AI-driven security solutions utilize machine learning algorithms that extract knowledge from past data. This can result in incorrect identification of hazards when the system comes across new, unfamiliar dangers that do not conform to established patterns. Another emerging issue is the potential for hackers to exploit AI technology for criminal activities, such as creating highly persuasive phishing emails and developing sophisticated malware.
What Skills Are Necessary To Implement AI In Cybersecurity?
The relationship between AI and cybersecurity has become increasingly intertwined. People who possess proficiency and talent in both areas are currently extremely sought after. Enterprises and technology organizations are seeking people who possess a comprehensive understanding of both cybersecurity and AI, enabling them to determine the appropriate application of AI approaches in cybersecurity workflows. Engineers, analysts, and data scientists with experience in cybersecurity are crucial. Skills in data modeling, language modeling, behavior analysis, and deep neural networks are essential for these positions. Furthermore, it is important that they possess a comprehensive comprehension of cybersecurity principles. Strong expertise in network security, data protection, malware detection and defense, computer forensics, and cryptography are prerequisites for becoming an AI cybersecurity specialist.
In the future, artificial intelligence (AI) will be integrated into the Security Operations Center (SOC) to enhance security and improve the productivity of operators. This will be achieved by training AI on extensive user behavioral data. Artificial intelligence (AI) will be an indispensable resource for security operations experts, aiding them in promptly detecting and recognizing potential dangers.




