Intel has revealed its latest lineup of computer chips, headlined by the Gaudi3, an artificial intelligence chip designed for generative AI software. Set to launch next year, Gaudi3 aims to challenge Nvidia and AMD’s chips that currently dominate the AI landscape, especially in powering large and resource-intensive AI models.
Prominent AI models, including OpenAI’s ChatGPT, heavily rely on Nvidia GPUs in the cloud, contributing to Nvidia‘s significant stock growth this year. In a bid to shift the dynamics, companies like AMD and Intel are introducing competitive chips to lure AI companies away from Nvidia’s market dominance.
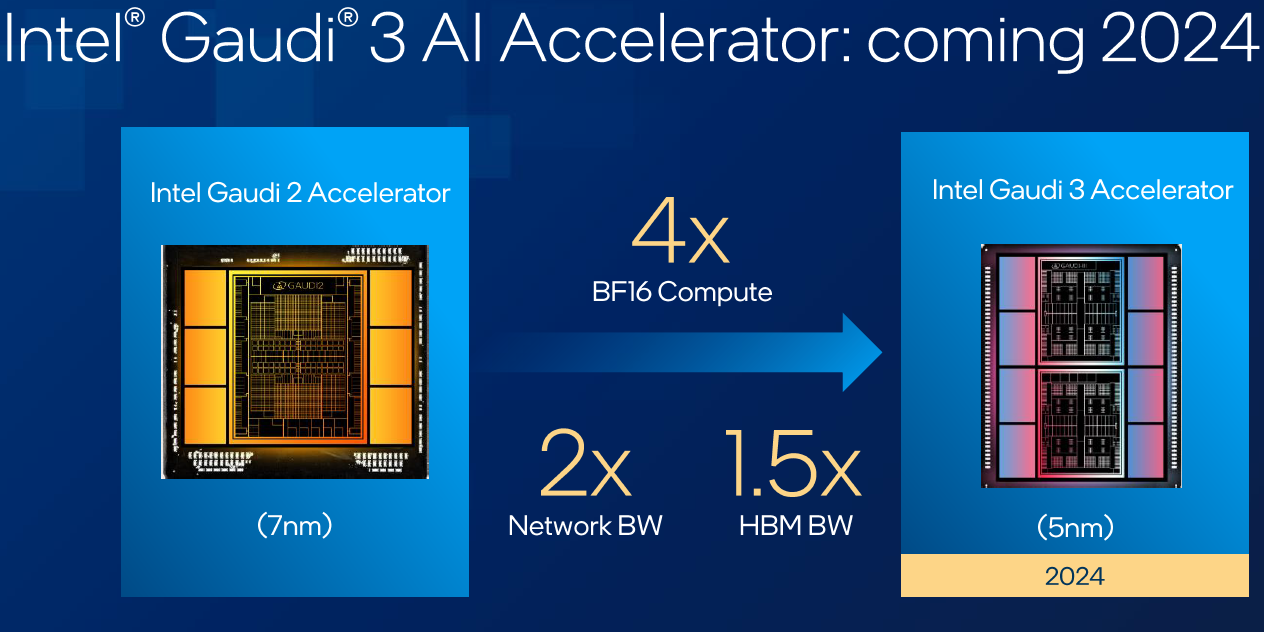
While details about Gaudi3 are limited, it is expected to compete with Nvidia’s H100 and AMD’s upcoming MI300X, scheduled for customer shipments in 2024. Intel’s Gaudi chips have been in development since 2019 when the company acquired chip developer Habana Labs.
At a launch event in New York, Intel CEO Pat Gelsinger highlighted the growing excitement around generative AI and predicted the rise of AI-powered PCs in the upcoming year. The announcement included Intel’s new Core Ultra processors, designed for Windows laptops and PCs, featuring a specialized AI component called an NPU for accelerated AI program execution.

The Core Ultra chips, built using Intel’s 7-nanometer process for enhanced power efficiency, may not match the capability of running internet-disconnected chatbots like ChatGPT but excel in handling smaller tasks. Additionally, they boast enhanced gaming capabilities and improved graphics performance, contributing to over 40% faster performance in applications like Adobe Premier.
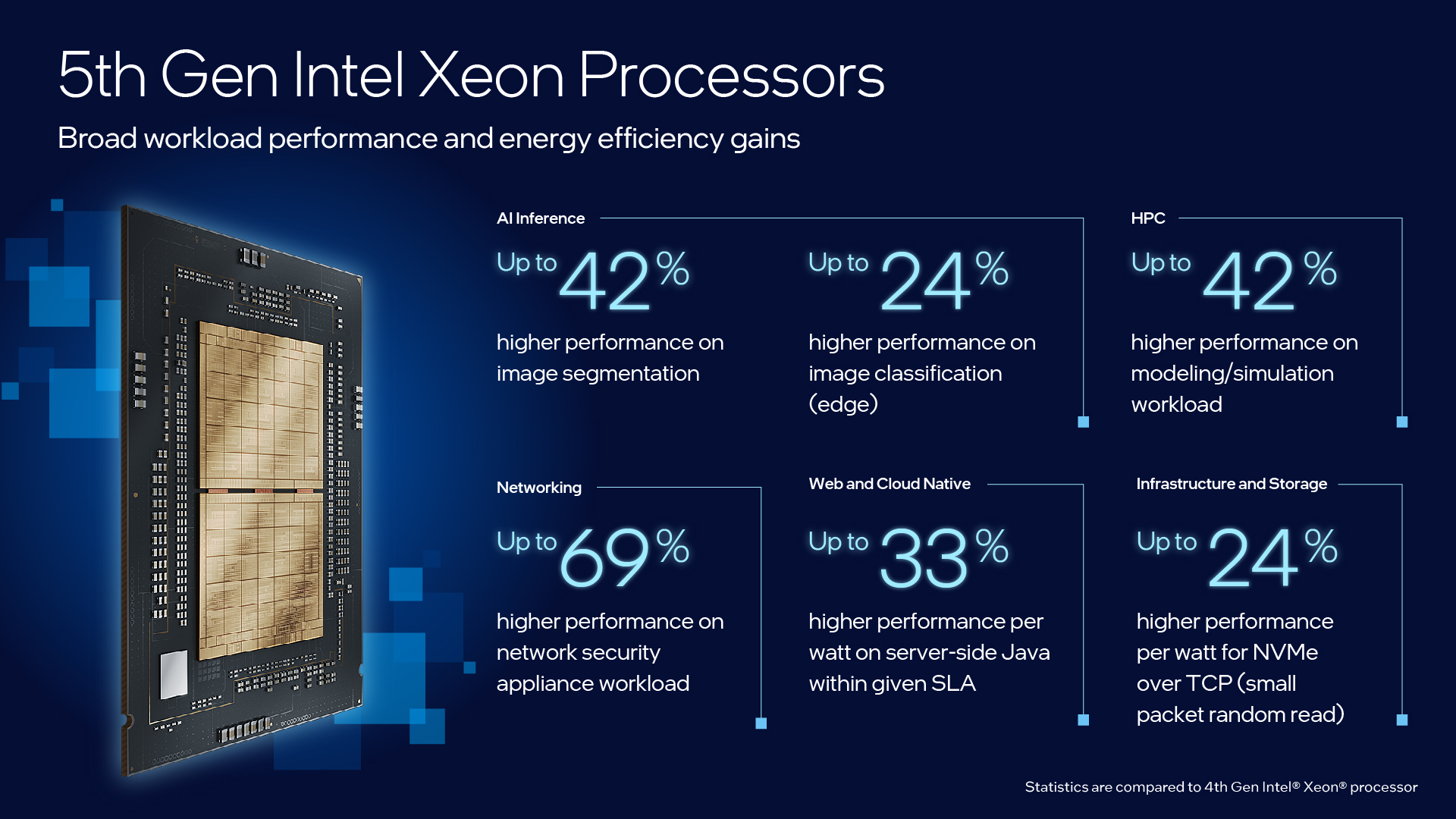
In addition to Core Ultra, Intel also introduced its fifth-generation Xeon server chips, crucial for large organizations and cloud companies. While pricing details were not disclosed, these processors are often coupled with Nvidia GPUs in systems used for training and deploying generative AI. The latest Xeon processor is optimized for inferencing, a less power-intensive process compared to AI model training. This move aligns with Intel’s strategy to catch up with Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Co. in chip manufacturing prowess by 2026.
In addition to more potent gaming capabilities, Core Ultra processors feature enhanced graphics processing power that can accelerate applications like Adobe Premier by over 40%. The laptops carrying the lineup debuted in stores on Thursday.
Cloud companies and other large organisations utilise servers powered by Intel Xeon processors of the fifth iteration. While Intel did not disclose the price, the previous Xeon set back thousands of dollars. Systems utilising Nvidia GPUs in conjunction with Intel Xeon processors are frequently employed to train and deploy generative AI. Eight GPUs are paired with one or two Xeon CPUs in certain systems.
According to Intel, the most recent Xeon processor will be especially effective for inferencing, or the deployment of an AI model, which consumes less power than training.